BENEFITS
Precise. Modular. Scalable.
Products in the Spotlight
Versatile Imaging Solutions
In the operating room and in practice, our imaging solutions provide access to enhanced visualization. With multiple configuration options, you can build image chains that align best with your needs and budget.
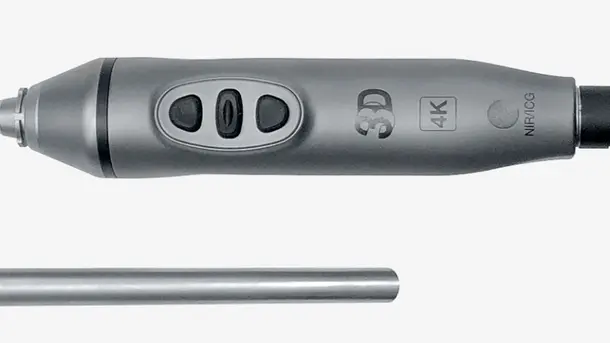
IMAGE1 S™ Rubina®
Combines 3D and 4K technology with NIR/ICG fluorescence imaging to supply high quality information and helps to improve detection and surgical precision. NIR/ICG expands the diagnostic options, for instance, perfusion assessment and detection of sentinel lymph nodes.
Enhanced Visualization
Discover visualization modes that helps to identify structures in a more differentiated manner.
The IMAGE1 S™ Rubina® product family

IMAGE 1 S™
In order to achieve the best possible treatment results, we offer you an appropriate solution that will help you better visualize your patient. With our modular, sustainable and customizable solution, we offer you a wide range of visualization options.
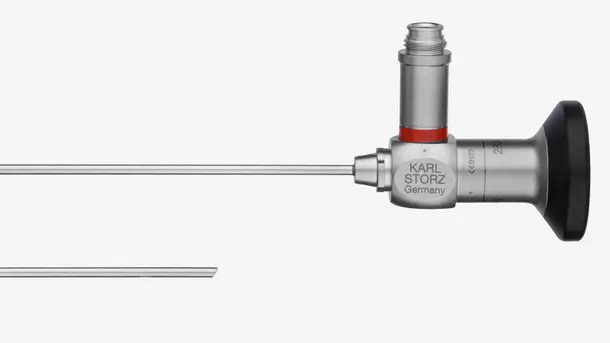
TIPCAM®1 Rubina®
This all-in-one video endoscope integrates three advanced imaging technologies – 4K, 3D and NIR/ICG into one single product for enhanced visualization and improved depth perception.

Power LED Rubina®
This laser-free cold light source, designed for white light and NIR/ICG applications provides durability and efficiency.
Complete your NIR/ICG imaging solution
Combine these technologies into one system to adapt to your needs
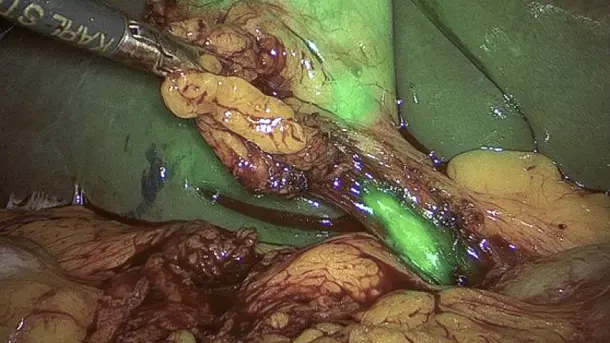
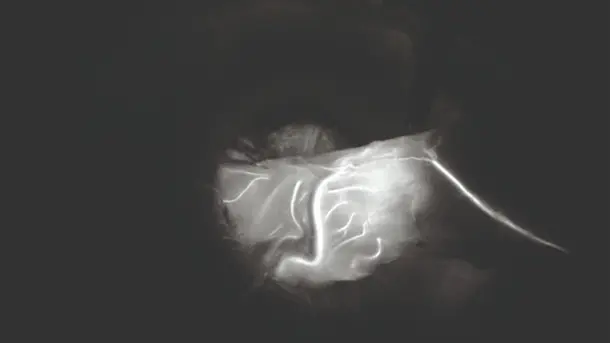
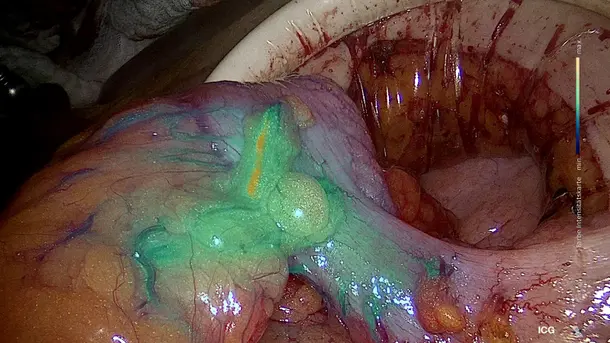
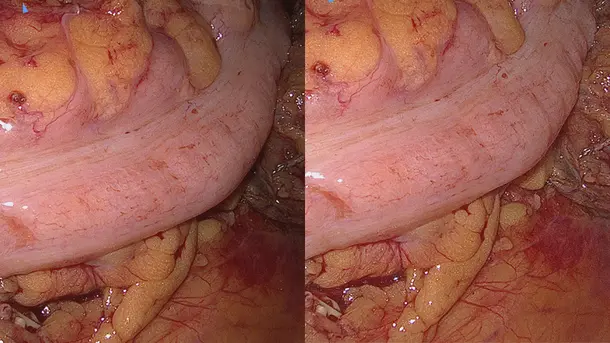
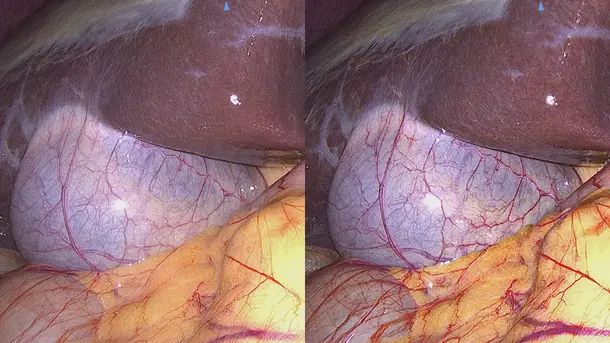
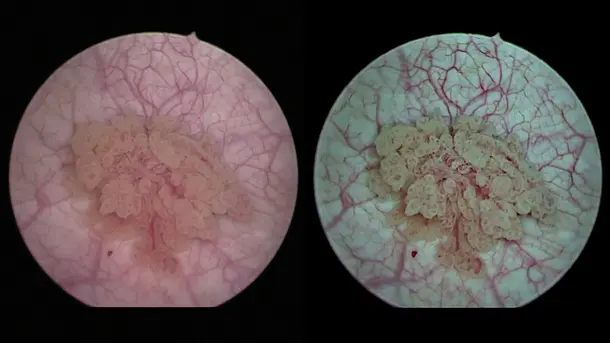
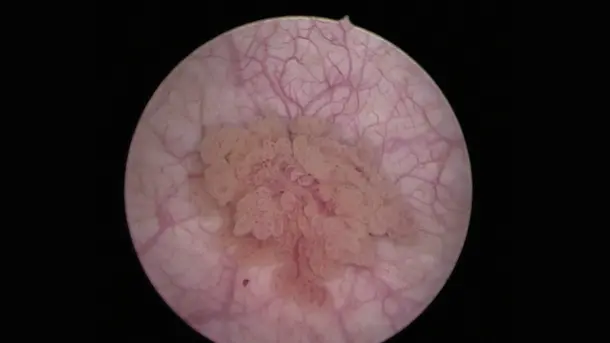
IMAGE1 S™ Rubina® application fields
Using the IMAGE1 S™ Rubina® System, we made a huge step ahead in fluorescence guided surgery moving from "darkness" to light in 4K 3D for better care of our patients.
IMAGE1 S™ 4U
With the introduction of 4K - which brought the next step in the development of endoscopic image quality - you are able to recognize and identify fine details during surgery and we pursue the goal of continuous optimization of image quality.
Enhanced Visualization
Discover visualization modes that help to identify structures in a more differentiated manner.
The IMAGE1 S™ 4U product family

IMAGE 1 S™
In order to achieve the best possible treatment results, we offer you an appropriate solution that will help you better visualize your patient. With our modular, sustainable and customizable solution, we offer you a wide range of visualization options.

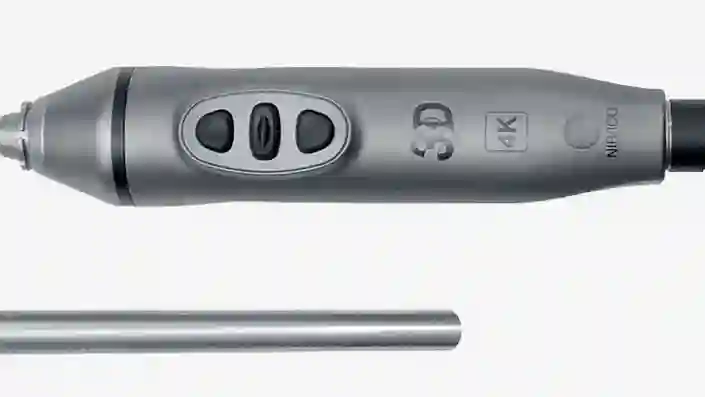
IMAGE1 S™ 4U Camera Head
This camera head is a key element for visualization and with its 4K resolution you benefit from a higher resolution and extended color space, to assist you with the identification and differentiation of structures.

POWER LED 300
This laser-free cold light source, designed for white light applications provides durability and efficiency.
Complete your 4K imaging solution
Combine these components into one system and adapt them to your needs.
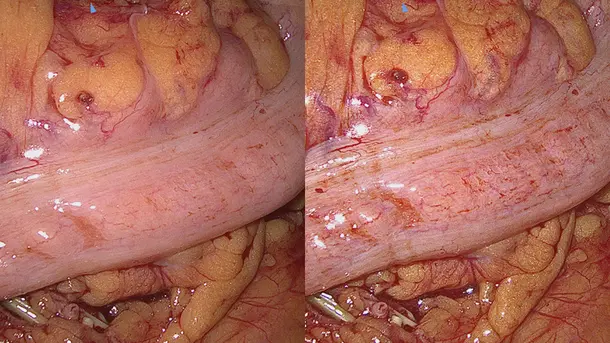
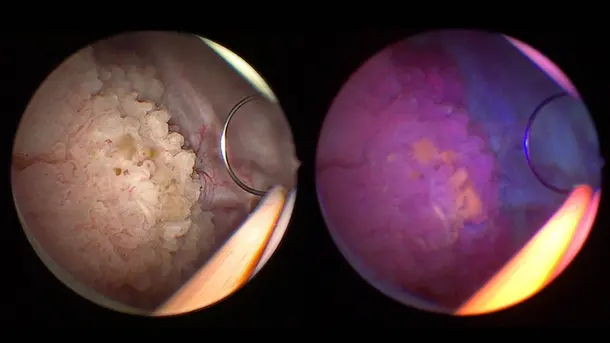
IMAGE1 S™ 4U Application fields
When the IMAGE1 S™ technology was introduced at our hospital, suddenly you saw things you`ve never seen before. When you see better, you can treat better.
IMAGE1 S™ Saphira™
Blue Light Imaging (BLI), formerly known as PDD, enables by administration of Hexvix/Cysview the visualization of early-stage malignant tumors that are difficult to see under white light diagnosis.
Enhanced Visualization
Discover visualization modes that help to identify structures in a more differentiated manner.
The IMAGE1 S™ Saphira™ product family

IMAGE 1 S™
In order to achieve the best possible treatment results, we offer you an appropriate solution that will help you better visualize your patient. With our modular, sustainable and customizable solution, we offer you a wide range of visualization options.

IMAGE1 S™ HX-P FI-Camera Head
This camera head is designed for Blue Light and white light applications, offering ergonomic working conditions due to its lightweight pendulum design.

POWER LED Saphira™
This laser-free cold light source, designed for white light and Blue Light Imaging applications provides durability and efficiency.
Complete your Blue Light Imaging solution
Combine these components into one system and adapt them to your needs.
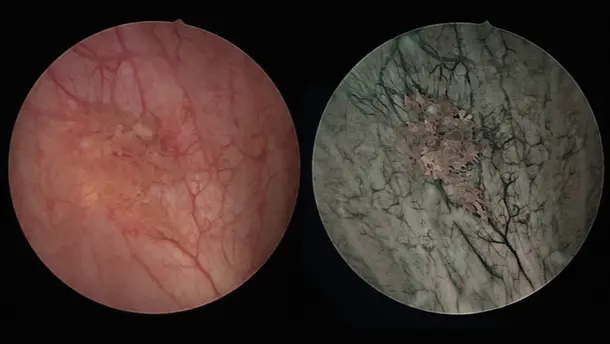
IMAGE1 S™ Saphira™ application field
In the last months, I have had the opportunity to use the new Saphira™ light source, which really ameliorates the quality of the procedure significantly.
TELE PACK+
Compact, diagnostic and procedural platform for small and diagnostic procedures with many compatibility options. Ideal for use in doctors´ offices, day clinics, emergency rooms, intensive care units, and outpatient settings.
The TELE PACK+ product family
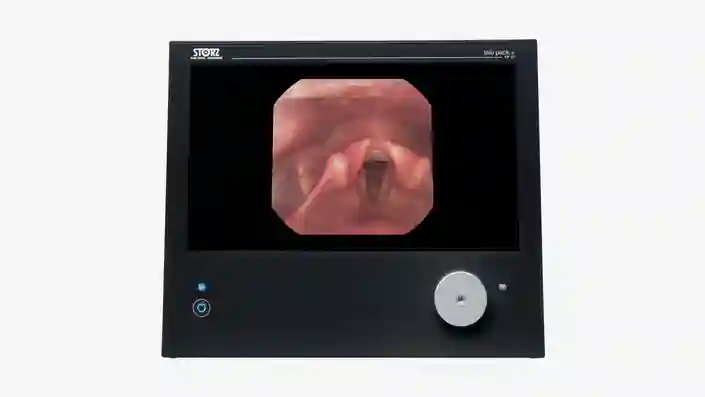
TELE PACK+
Experience the benefits of a compact and easy to carry unit, which combines a monitor, LED light source, camera control unit and documentation with integrated network functionality.

X-Line and C-Line
With its X-Line and C-Line plugs, the TELE PACK+ is compatible with a wide range of rigid, flexible and single-use endoscopes, making it adaptable for use in almost all medical specialties.
Complete your FULL HD compact imaging solution
Combine these components into one system and adapt them to your needs
TELE PACK+ application fields
We like the new TELE PACK+ very much because it has brilliant image quality, which is very effective in diagnosis, especially in difficult cases.
TELECAM C3
The TELECAM C3 is ideal for small and diagnostic procedures in private practices and other surgical environments. It is suitable for use with a wide range of compatible endoscopes and can be used in almost all disciplines.
The TELECAM C3 product family

TELECAM C3
Benefit from our cost-efficient and compact camera control unit, designed for basic endoscopy procedures, with two camera connections that ensure compatibility with a wide range of endoscopes.

X-Line and C-Line
With its X-Line and C-Line plugs, the TELECAM C3 is compatible with a variety of rigid, flexible and single-use endoscopes, making it adaptable for use in almost all medical specialties.

POWER LED 175
This laser-free cold light source, designed for white light applications in smaller cavities provides durability and efficiency.
Complete your FULL HD imaging solution
Combine these components into one system and adapt them to your needs.
TELECAM C3 application fields
Create state-of-the-art surgical spaces tailored to your needs
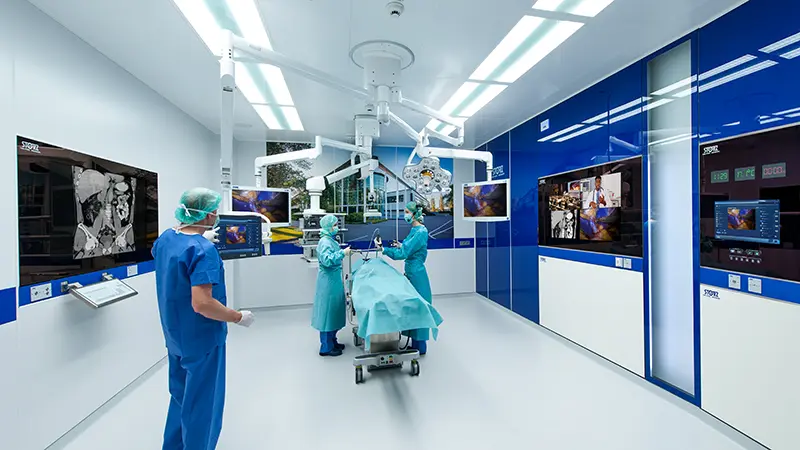
The future of operating room integration
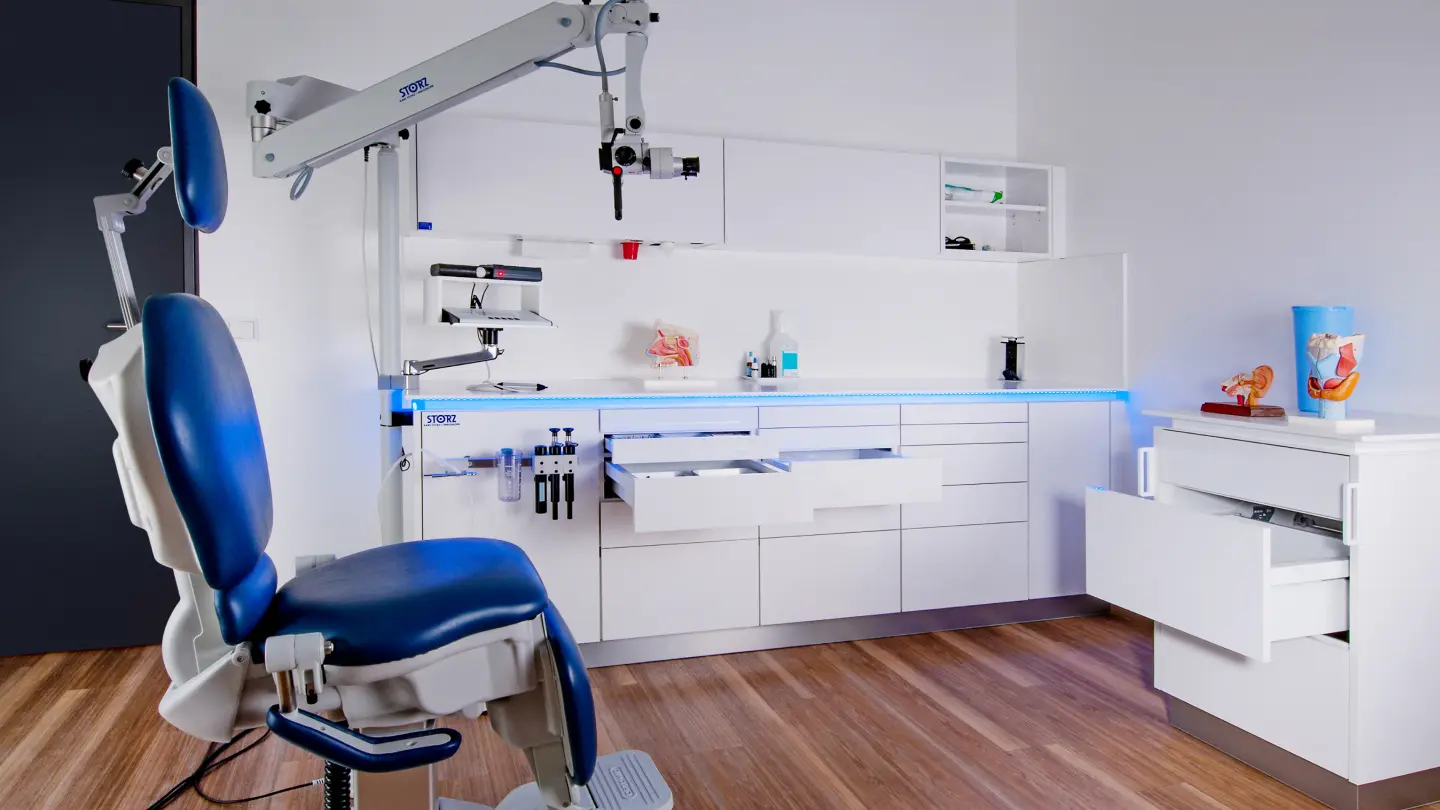
Modular interiors for your practice
Empowering through education
CONTACT Get in touch with our specialists
We'll guide you through the whole process and help customize the right solution for your surgical needs.