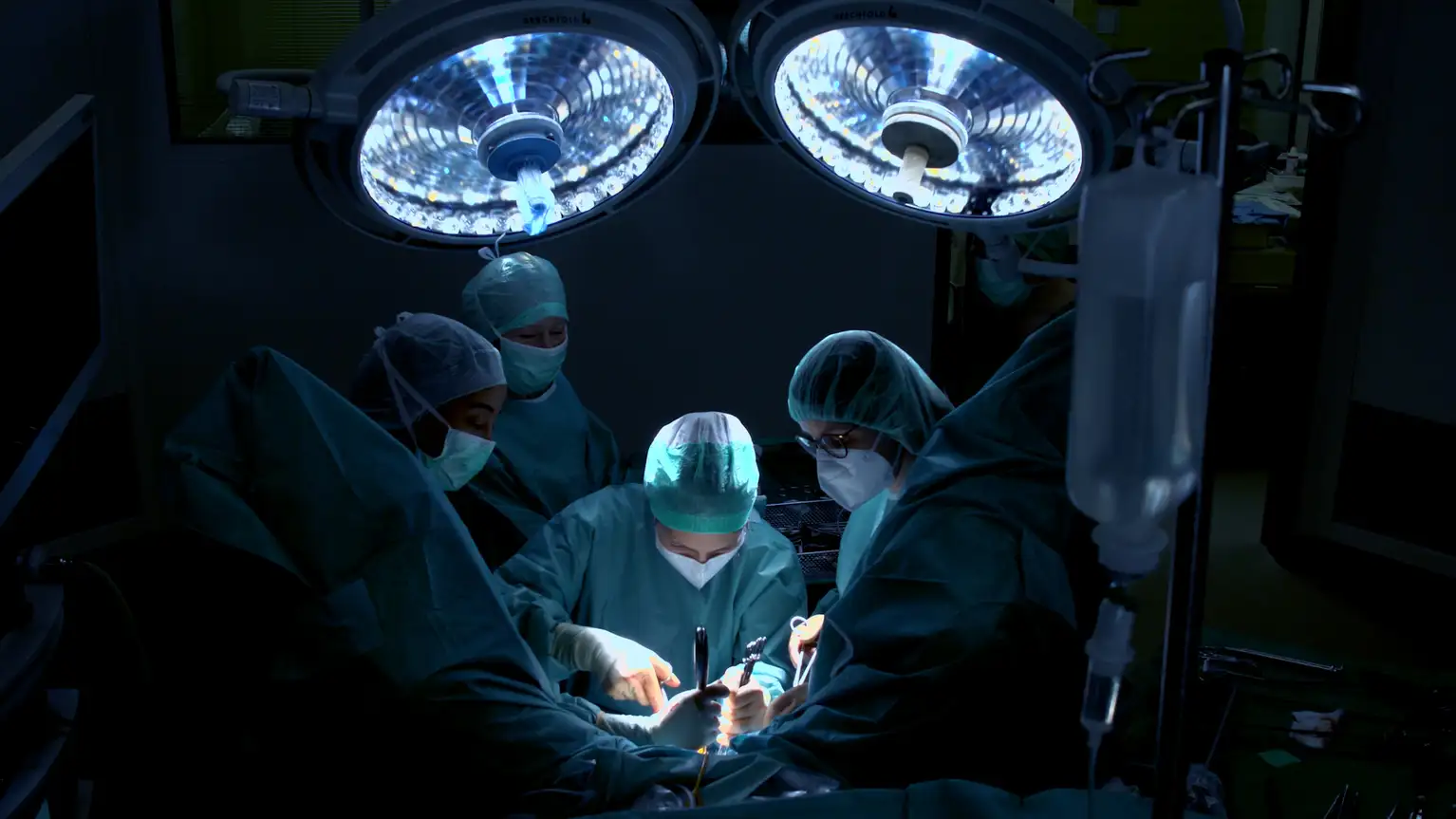
BENEFITS
Efficient. Cost-Saving. Empowering.
Products in the Spotlight
Highlights by procedure
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy has long been considered the gold standard for diagnosing and treating intrauterine diseases. Our role in the miniaturization of hysteroscopes has helped surgeons around the world perform procedures outside the OR, even without general anesthesia.
Everything you’ll need to get started
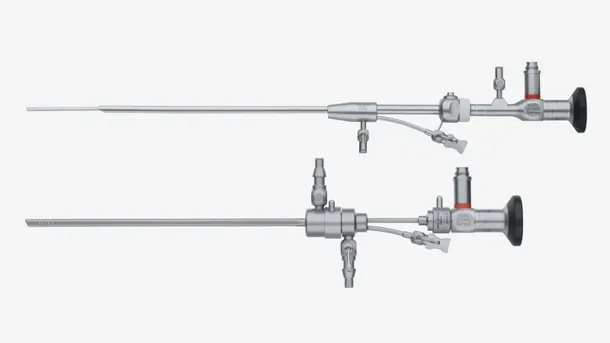
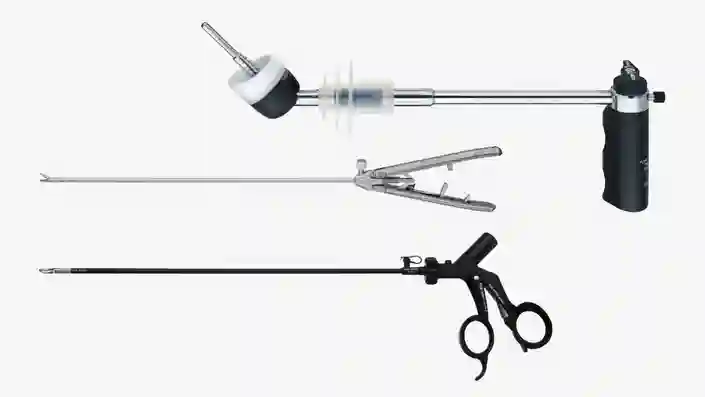
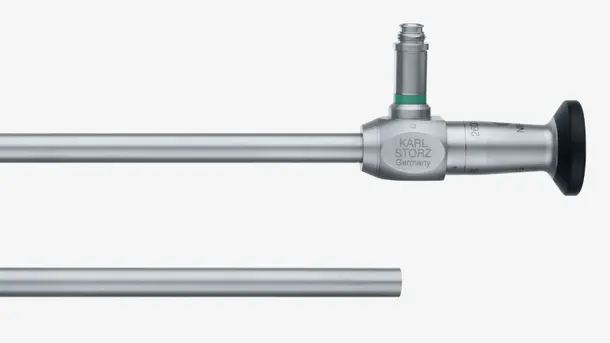
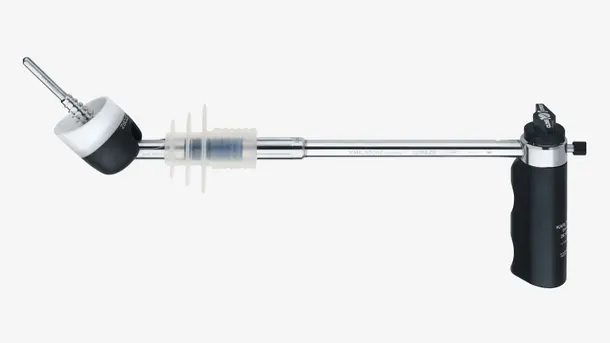
Hysteroscopy set-up
Create your personalized set-up. Explore our broad range of hysteroscopes for diagnostic as well as see & treat procedures.
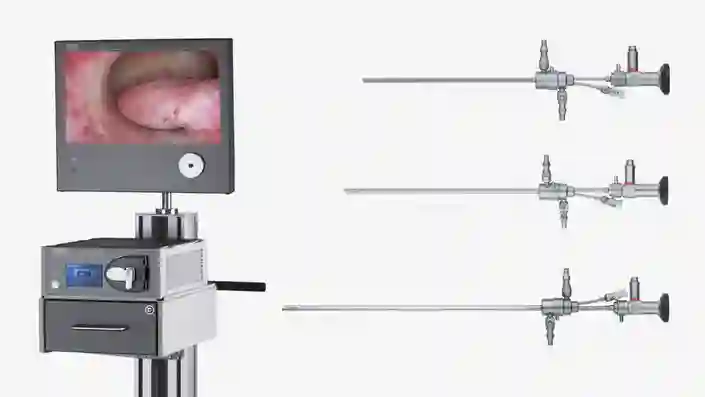
Digital Hysteroscopy Clinic (DHC)
The concept of DHC, first introduced by Dr. Rudi Campo is aimed combining ultrasound with hysteroscopy for a one-stop diagnostic procedure and surgical approach, offering increased surgical performance in an outpatient setting. Currently the largest DHC is the CLASS Hysteroscopy Center located in Rome, Italy.5
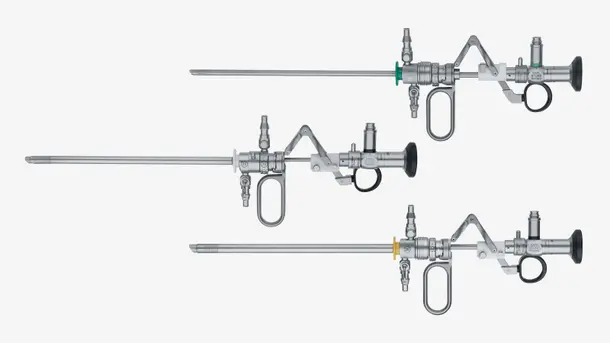
Highlights from our range
Laparoscopy
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) plays an essential role in gynecology and is used in multiple areas such as benign procedures, urogynecological surgery, or specific oncological interventions. The latest camera technologies such as 4K, 3D and fluorescence imaging are the benchmark in modern gynecological laparoscopy. In addition to the general laparoscopic set-up, a variety of equipment specially designed to assist surgeons during gynecologic procedures is offered.
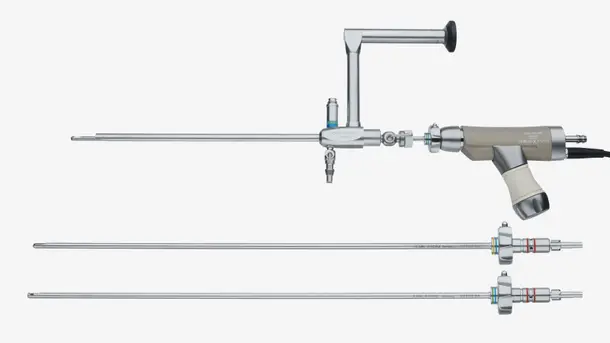
Everything you’ll need to get started
Highlights from our range
Fetoscopy
The KARL STORZ suite of products for minimally invasive surgeries includes a range of devices that are well suited for various fetoscopic interventions, including the treatment of twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome and congenital diaphragmatic hernia, amongst many others.
Everything you’ll need to get started

Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome
Choose your suitable model from a variety of different sizes for anterior and posterior placenta.
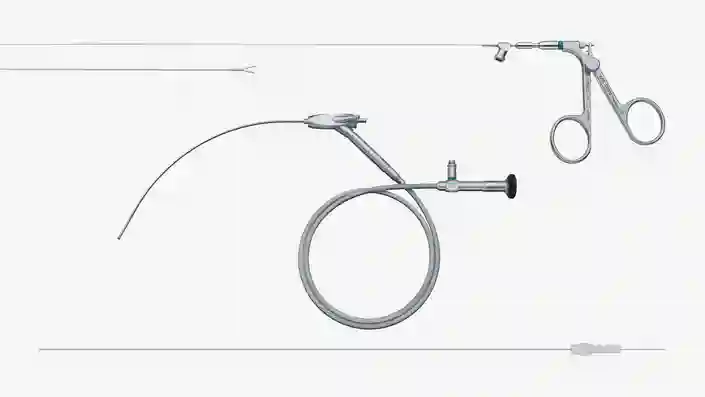
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
Fetal Endoluminal Tracheal Occlusion (FETO) is a prenatal minimally-invasive procedure to treat the fetus in cases of congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
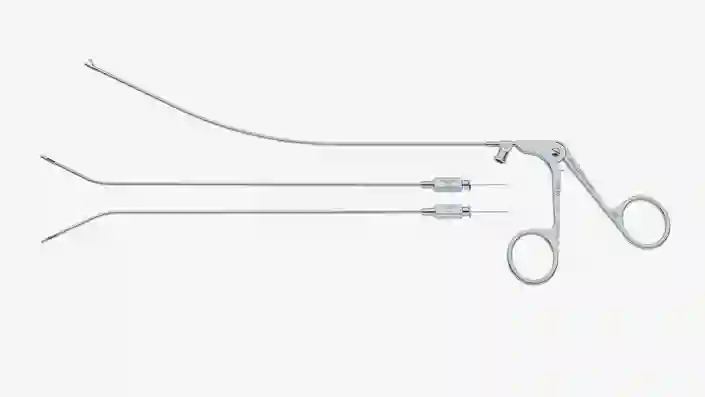
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
For Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS), the sample can be removed either by aspiration or with a grasping forceps.
Colposcopy
With the help of the VITOM® colposcope, precancerous cervical lesions are transparently displayed and visible for both the examiner and the patient. This modern and ergonomic approach fosters the integration of the patient in the diagnostic process and the subsequent therapeutic strategy. In addition, the VITOM® can be used for electrosurgical loop excision (LEEP) under magnified vision and for the visualization of both open and vaginal interventions.
Everything you’ll need to get started
Transvaginal Endoscopy
The benefits of transvaginal endoscopy are many, including direct access to the ovarian fossa and tubo-ovarian organs without extra manipulation. This technique allows the examination of the female reproductive tract and combines a transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy, hysteroscopy and salpingoscopy.
Everything you’ll need to get started
Endoscopic Training
Scientific evidence indicates that dry lab training for endoscopic surgical skills, prior to training in the operating room, improves patients’ post-operative well-being substantially. Besides the support of various endoscopic training initiatives globally, KARL STORZ offers various training options, ranging from specialized in-house training equipment to new KARL STORZ Online Suturing Courses.
Everything you’ll need to get started

Laparoscopic Training
Learn more about our training equipment to improve laparoscopic psychomotor and suturing skills.

Hysteroscopic Training
Learn more about our training equipment for hysteroscopic psychomotor skills.
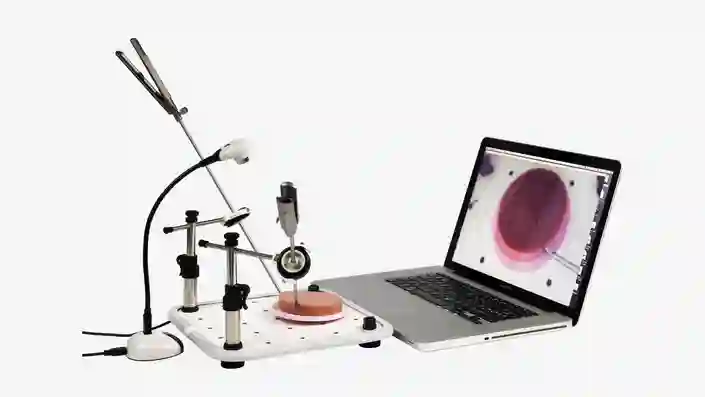
KARL STORZ Online Suturing Course
Practice makes perfect. Train your staff in laparoscopic suturing best practices through our 5-day courses.
Create state-of-the-art surgical spaces tailored to your needs
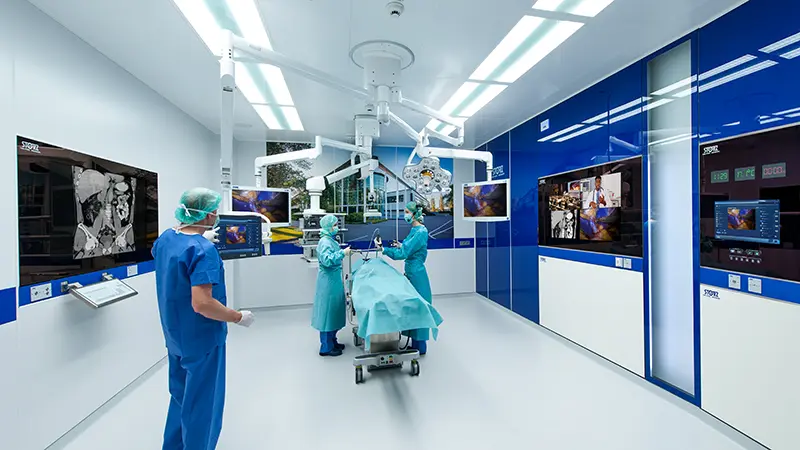
The future of operating room integration
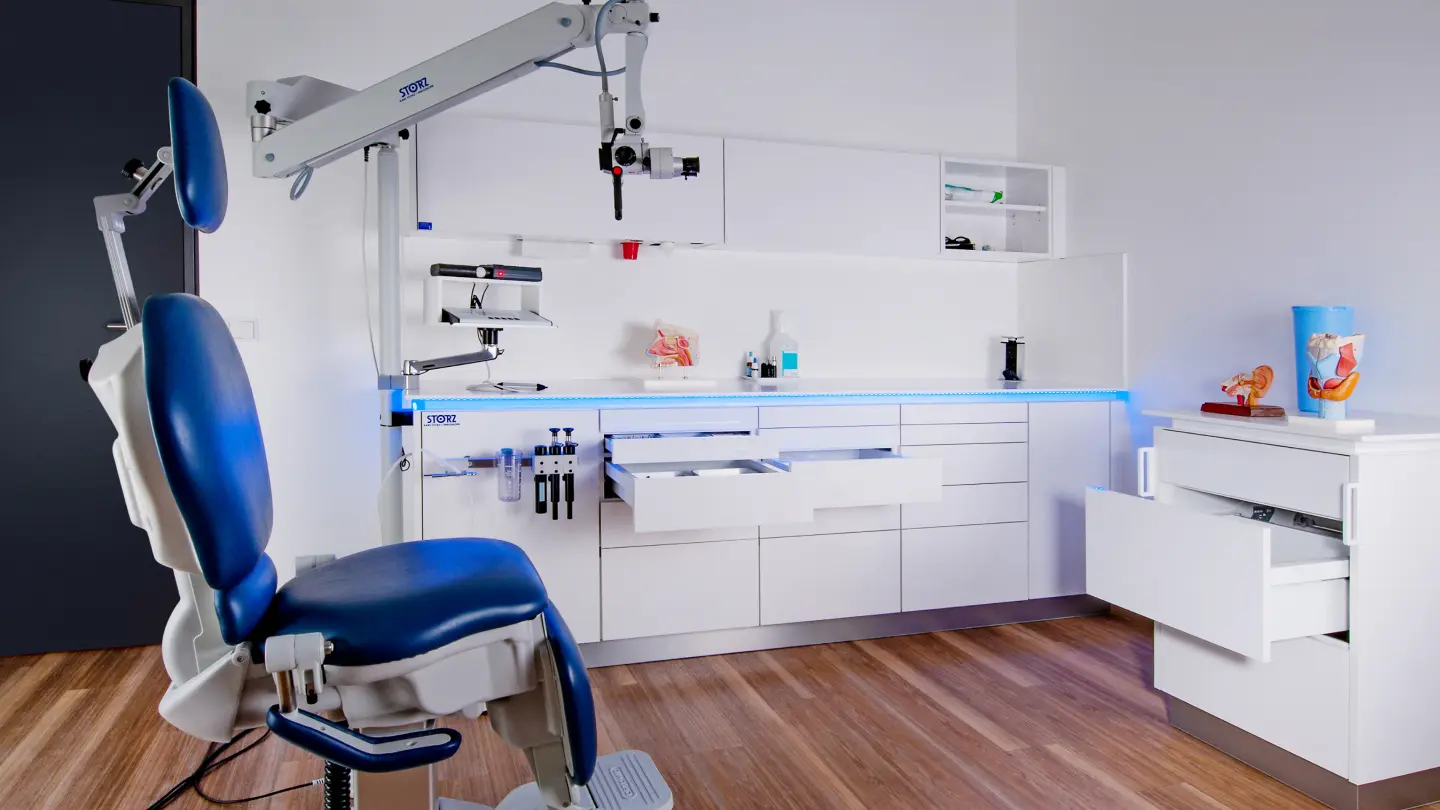
Modular interiors for your practice
Empowering through education
CONTACT Get in touch with our specialists.
At KARL STORZ, we recognize that every surgical need is unique, and we are committed to providing personalized assistance for all your requirements. Get in touch with us below for guidance on choosing the right products for your practice.