Secondary Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Ridge Sign
Mountain ridges border the Vierwaldstätter lake in the Swiss mountains.

Ridge sign.
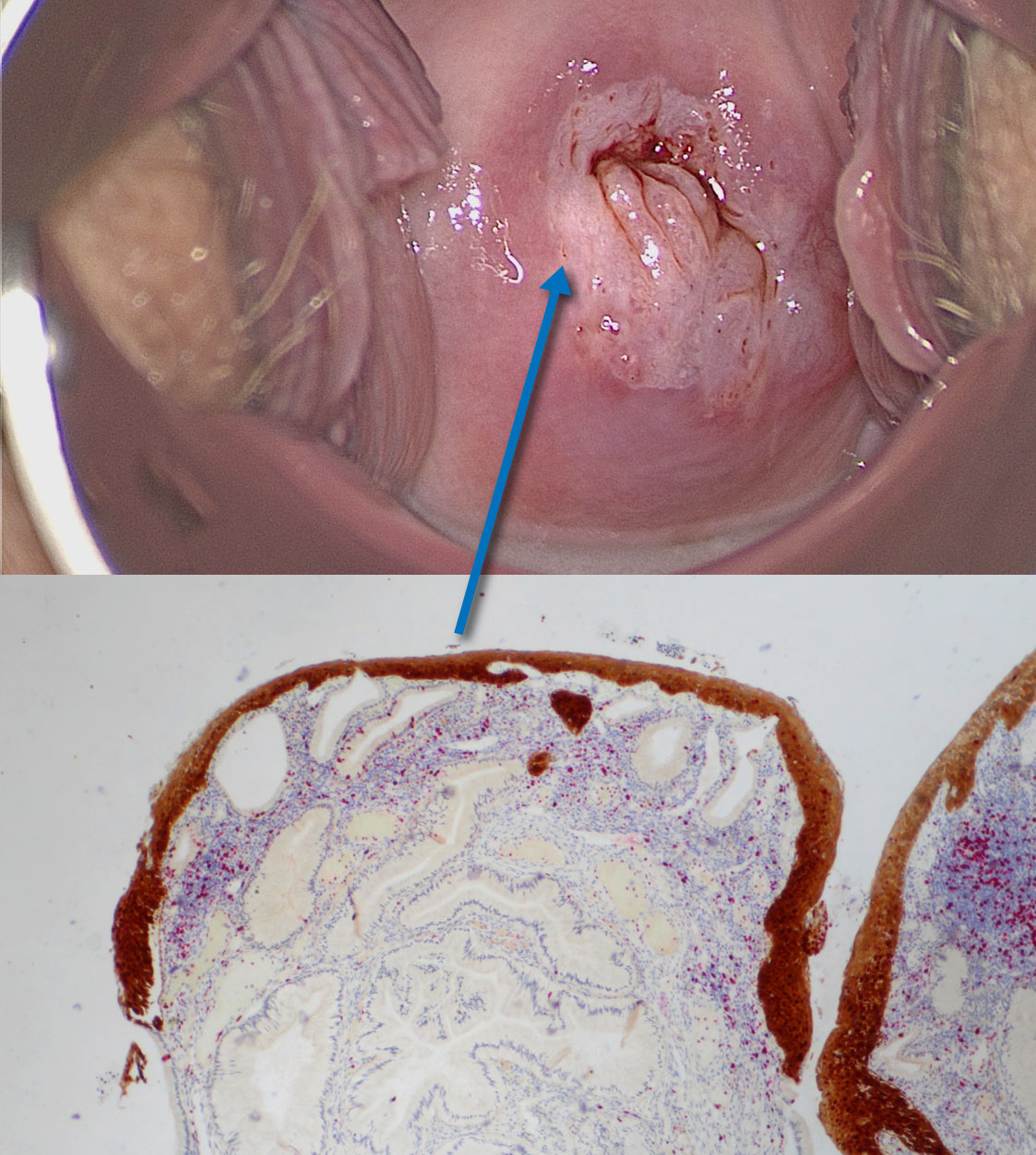
Ridges are also seen on the uterine cervix: ridge sign identified by colposcopy is reproduced in the histologic section taken from a ridge which is diagnosed as
Prominent ridges must be opaque to be called ‘ridge sign’.
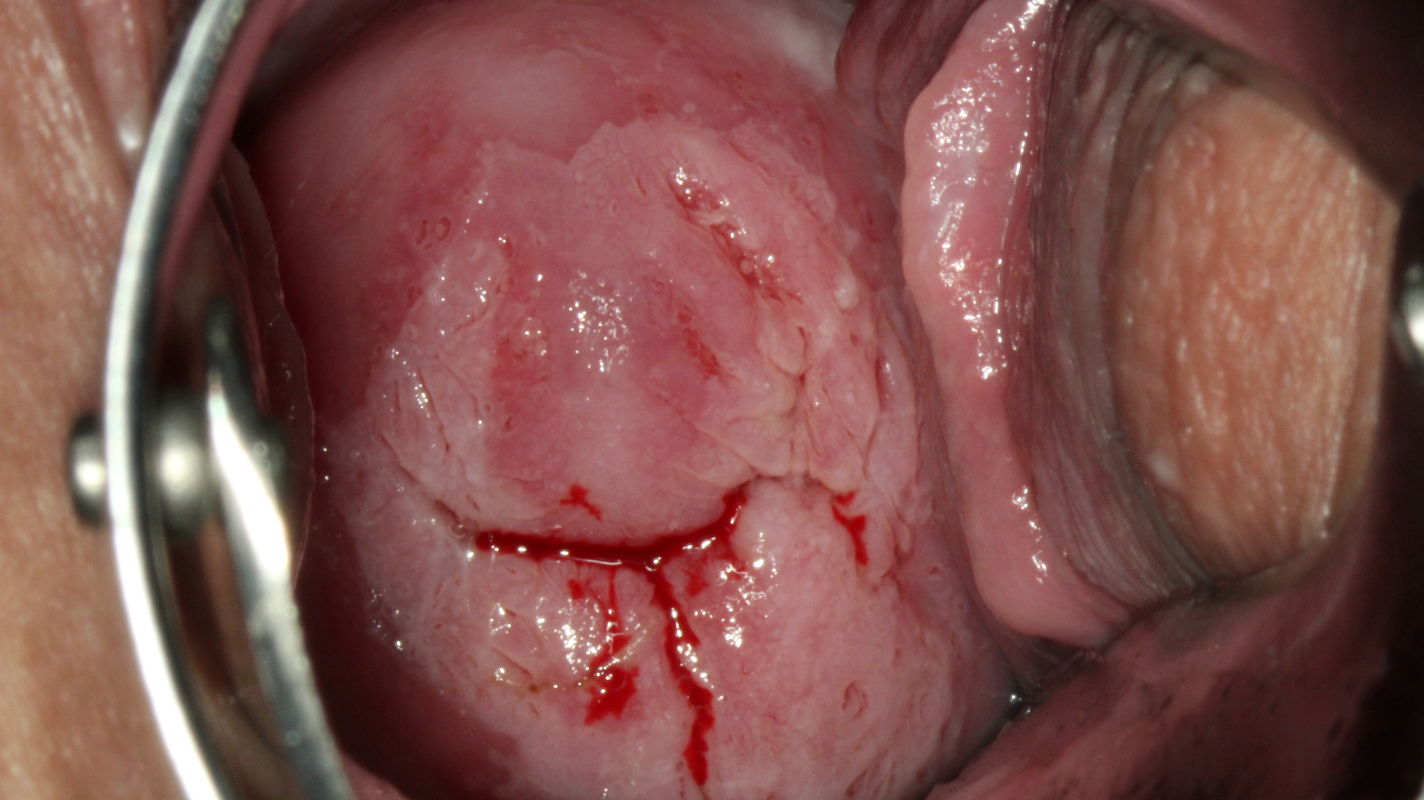
The ridge sign is also considered pathognomonic for HSIL:
Colposcopic findings in a 25-year-old gravida 1, para 0 with no prior history of disease.
The smear was reported as class IVa-p, and high risk HPV DNA and RNA were detected. Colposcopy shows a circular acetowhite lesion with opaque ridges directly at the squamocolumnar junction between 1 and 5 o’clock and 9 and 11 o’clock in an atypical
Ridge containing HSIL overlaps and borders columnar epithelium.
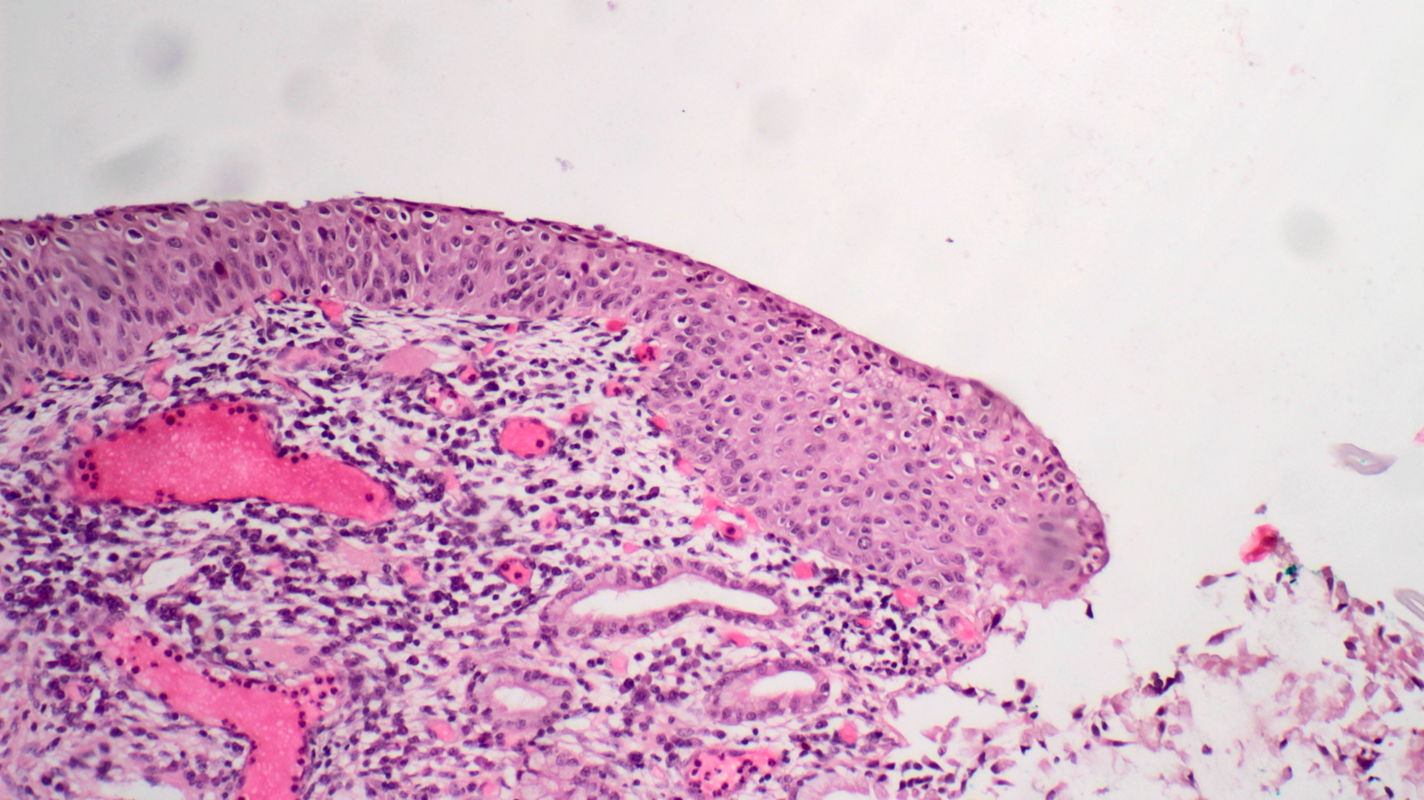
H&E stain of tissue sampled from the ridge lesion at 5 o’clock by punch biopsy shows atypical cells that uniformly occupy the full width of the epithelium and are indistinguishable from the surface cells. We clearly see the termination of atypical epithelium at its junction with columnar epithelium. The diagnosis is grade 3 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN 3).