Secondary Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Examples of Transformation Zones
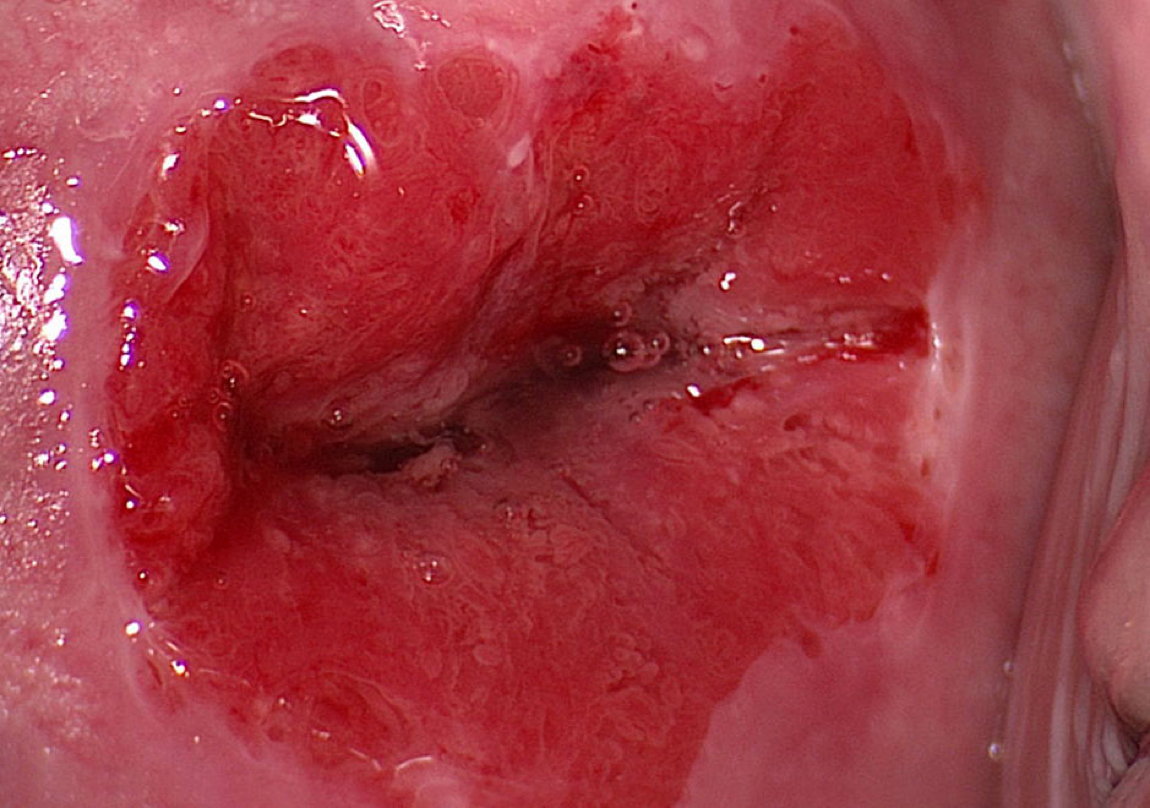
The squamocolumnar adult or functional junction is fully visible, presenting the columnar epithelium in red color prior to application of acetic acid.
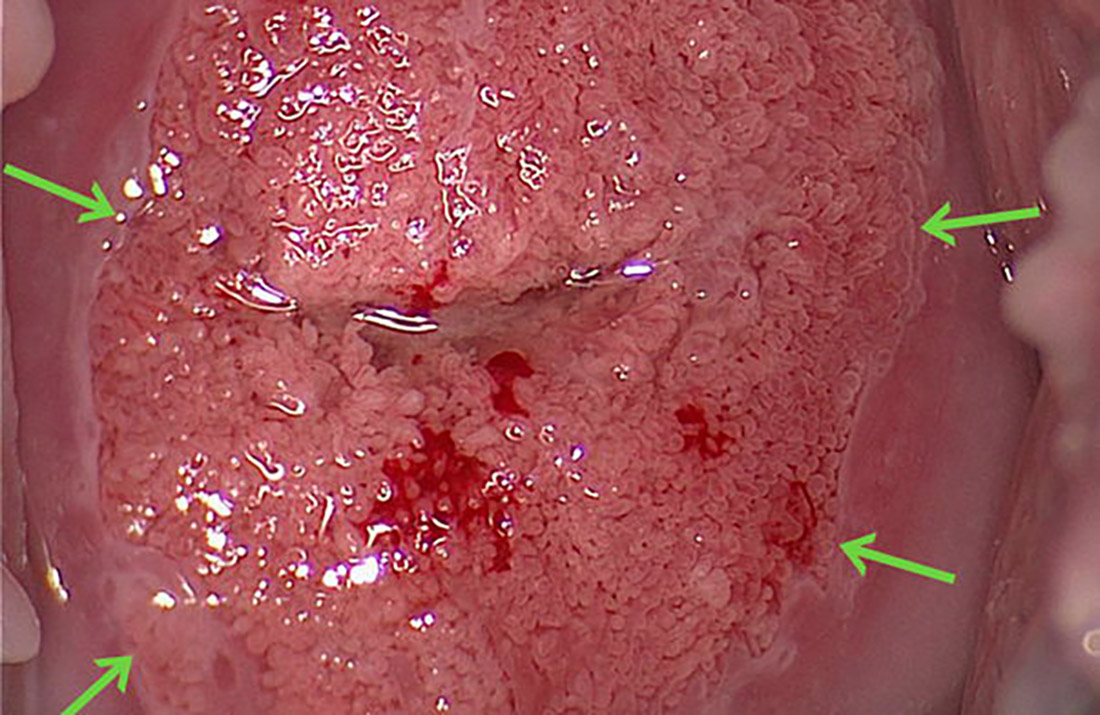
Following application of acetic acid, aceto-white columnar epithelium borders directly on squamous epithelium, the major features of a normal transformation zone. In this adolescent, the squamocolumnar junction indicated by green arrows is identical with the congenital junction.
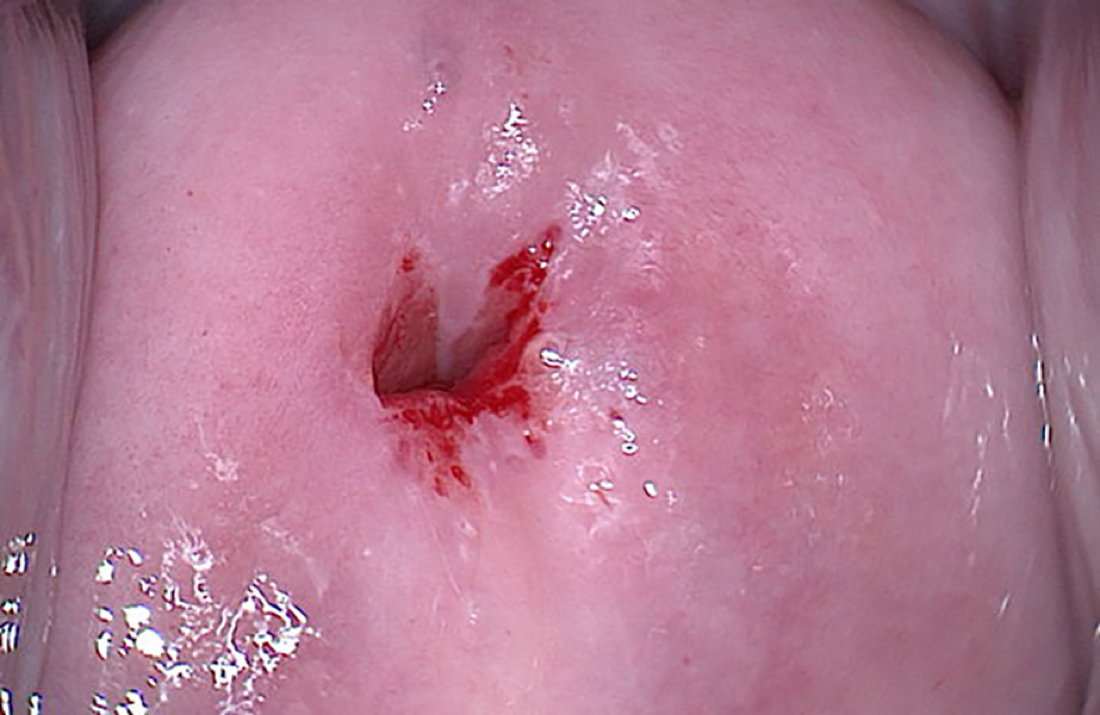
The adult or functional squamocolumnar junction is fully visible and a small tongue of squamous epithelium expands into the cervical canal at 12 o’clock.
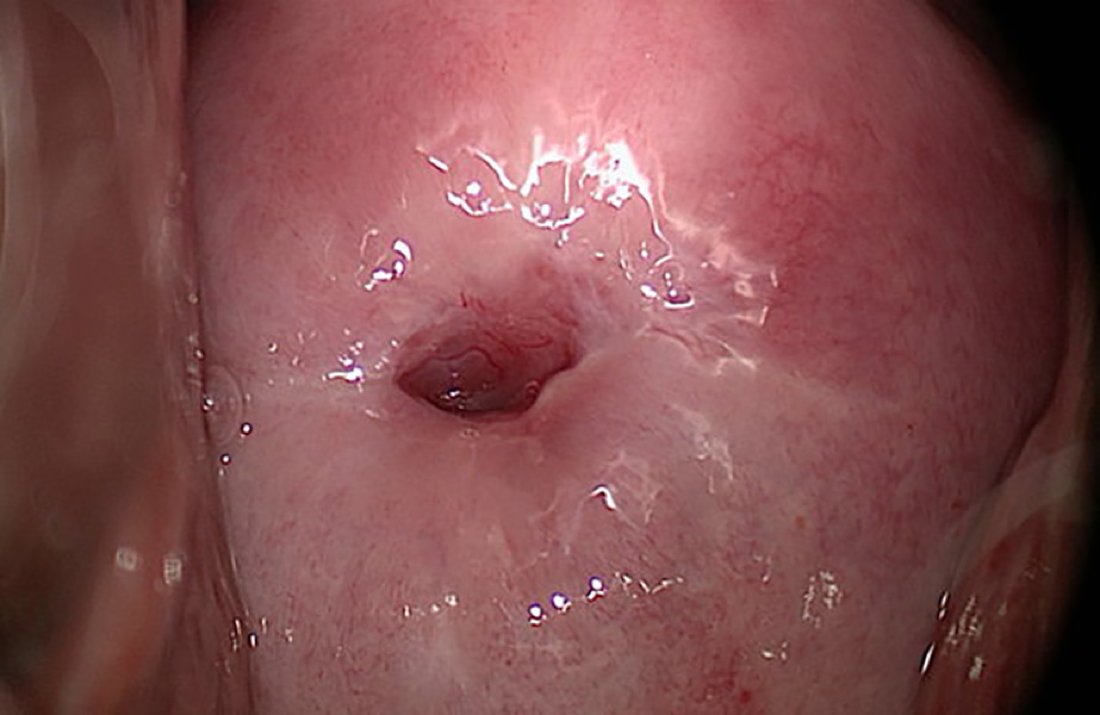
The adult or functional squamocolumnar junction is located inside the endocervix and is therefore invisible to the colposcopist. Thus, by definition colposcopic findings are inconclusive.